All rights reserved © 2026
Keeping up to date device drivers avoids instability in the system, hardware conflict and poor performances. Although the number of users served by IObit Driver Booster Pro is in the millions, other solutions have their own benefits with regard to certain workflow and technical needs.
The contemporary windows operating systems are interrelated with thousands of hardware devices, each having driver specifications provided by the manufacturer. Obsolete drivers cause accidents, incompatibility and security risks. The professional driver management softwa(as IObit Driver Booster Pro) re automates the detection, downloading and install processes and minimizes the system disruption.
Critical Evaluation Criteria:
Category: Open-source, completely free
Database Coverage: 160,000+ drivers with offline capability
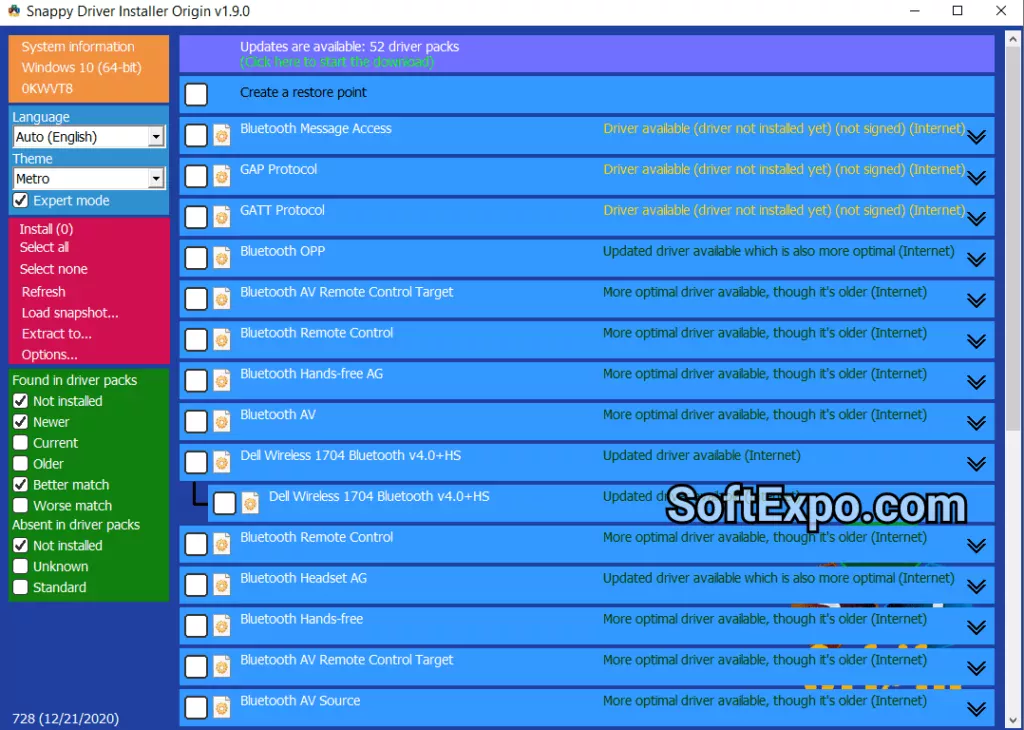
Snappy driver installer origin is the best open-source driver management. In contrast to commercial options, SDI Origin is not a real-time system since it is not dependent on the internet once the driver packs have been downloaded, and therefore it is priceless to systems that do not have consistently active internet connections.
Key Advantages:
Optimal Use Cases:
Technical Considerations:
Interface complexity may overwhelm casual users. The comprehensive approach requires understanding driver compatibility and system architecture. Download size for complete driver packs exceeds 20GB.
Category: Freemium (free version with limitations)
Database Coverage: 2,300,000+ drivers
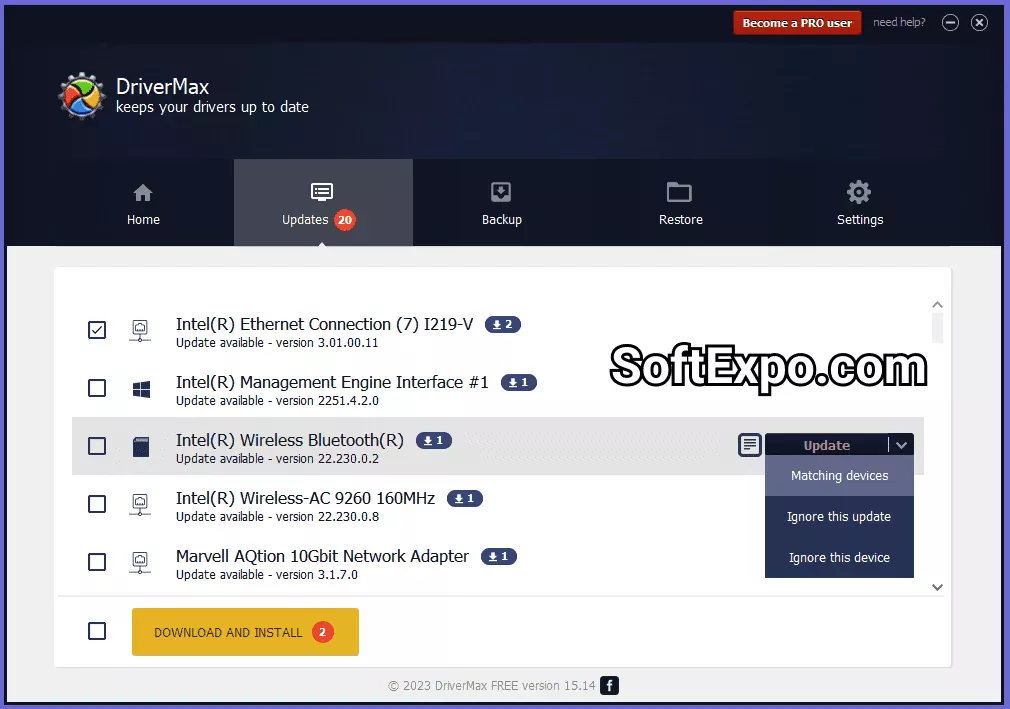
DriverMax balances accessibility with professional features. The free tier permits two driver downloads daily, while the PRO version removes restrictions and adds scheduling capabilities.
Key Advantages:
Optimal Use Cases:
Limitations:
Free version’s daily download restrictions hinder bulk updates. PRO subscription required for unlimited downloads and automatic scheduling.
Category: Freemium
Database Coverage: 8,000,000+ drivers
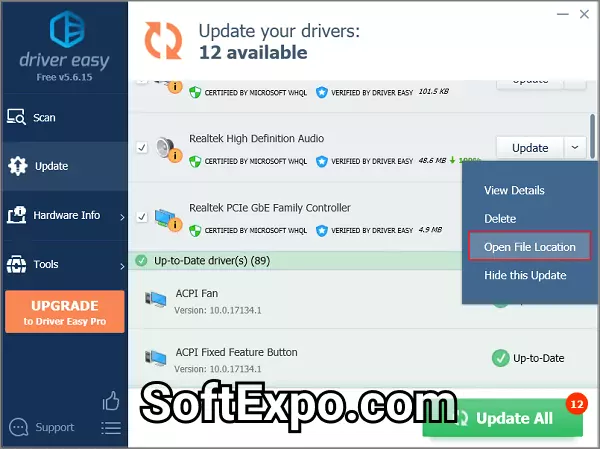
Driver Easy is focused on ease of use with no compromising technical performance. The scanning engine is able to identify obscure hardware accurately especially legacy components and special purpose peripherals.
Key Advantages:
Optimal Use Cases:
Pricing Structure:
Free version requires manual, individual driver downloads. PRO version enables batch processing and priority support.
Category: Commercial (free trial available)
Database Coverage: 450,000+ drivers
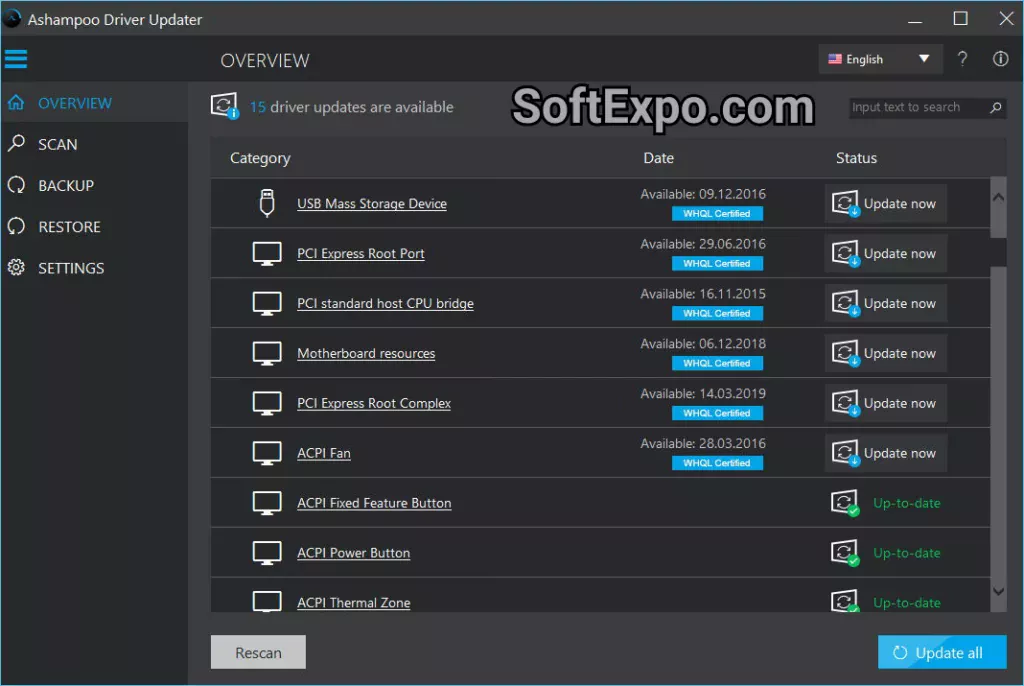
Ashampoo’s streamlined approach prioritizes stability over volume. The conservative update strategy reduces risk while maintaining system health through verified driver releases.
Key Advantages:
Optimal Use Cases:
Technical Approach:
Ashampoo prioritizes WHQL-certified drivers and avoids beta releases, reducing bleeding-edge hardware support but maximizing stability.
Category: Commercial
Database Coverage: 160,000+ WHQL-tested drivers
ITL Driver Updater focuses exclusively on Microsoft-certified drivers, eliminating compatibility concerns at the cost of reduced coverage for cutting-edge hardware.
Key Advantages:
Optimal Use Cases:
Certification Focus:
WHQL (Windows Hardware Quality Labs) certification ensures Microsoft validation, reducing driver-related system failures significantly.
Category: Commercial with free trial
Database Coverage: 500,000+ drivers
Auslogics Driver Updater integrates driver management within broader system optimization capabilities. The unified approach benefits users seeking comprehensive PC maintenance.
Key Advantages:
Optimal Use Cases:
Avast Driver Updater Category: Commercial
Database Coverage: 500,000+ drivers
Leveraging Avast’s security expertise, this solution emphasizes driver security alongside currency. Integration with Avast security products provides unified system management.
Key Advantages:
Optimal Use Cases:
Recommended: Snappy Driver Installer Origin
Open-source transparency, offline capability, and comprehensive control justify the steeper learning curve. Portable operation enables deployment across multiple systems without licensing concerns.
Recommended: ITL Driver Updater or Ashampoo Driver Updater
WHQL certification and conservative update strategies minimize disruption in production environments. Predictable licensing and support structures suit corporate procurement.
Recommended: Driver Easy or DriverMax
Balanced feature sets, intuitive interfaces, and reasonable pricing serve typical household needs. Free tiers provide value for systems with minimal update requirements.
Recommended: Snappy Driver Installer Origin or DriverMax Free
Zero-cost solutions deliver professional results. SDI Origin provides unlimited functionality, while DriverMax Free suits low-frequency update scenarios.
Recommended: Driver Easy
Extensive database and superior hardware detection algorithms excel at identifying and updating older components that other solutions overlook.
Conservative Approach (Recommended):
Aggressive Approach:
Risk: Introducing instability in working systems
Manufacturers occasionally release problematic drivers. “If it isn’t broken, don’t fix it” applies particularly to stable driver configurations. Update only when addressing specific issues or seeking confirmed improvements.
Risk: Installing older drivers marked “newer”
Date-based sorting doesn’t always reflect actual version progression. Manufacturers sometimes release patches with earlier dates than problematic releases. Verify version numbers against manufacturer documentation.
Risk: Missing optimized drivers and firmware
Graphics card manufacturers (NVIDIA, AMD) provide dedicated utilities with gaming optimizations and features unavailable through generic driver updaters. Use specialized tools for critical components.
Risk: Inability to recover from problematic updates
Driver installations occasionally fail catastrophically. Without backups, system recovery requires clean installations. Always create restore points or full backups before significant driver updates.
Risk: Installing beta or incompatible drivers
Automated tools occasionally suggest inappropriate drivers. Research unfamiliar updates, particularly for critical components. Manufacturer websites provide authoritative driver information.
Windows Update delivers tested drivers for millions of hardware configurations. While not comprehensive, Microsoft’s driver distribution provides:
Limitations:
Windows Update suffices for mainstream hardware and non-technical users. Specialized requirements justify third-party solutions.
Windows requires signed drivers for 64-bit systems. Legitimate driver update software respects signature requirements. Disabling enforcement creates security vulnerabilities and should be avoided except for specific development scenarios.
Generic drivers provide baseline functionality but omit hardware-specific features. Graphics cards, audio interfaces, and specialized peripherals require manufacturer drivers for full capability utilization.
Enthusiast users sometimes prefer cutting-edge drivers for performance improvements or new features. Beta drivers introduce instability risks unsuitable for production systems. Maintain separate test environments for experimental drivers.
Virtual machines require different drivers than physical hardware. Driver update utilities may suggest inappropriate drivers for virtualized environments. Understand your system’s virtualization status before updating.
Free software often monetizes through data collection. Review privacy policies before installation. Open-source solutions like SDI Origin provide transparency unavailable in commercial products.
Some driver updaters include promotional software or browser extensions. Careful installation monitoring prevents unwanted additions. Reputable solutions offer clean installation options.
Drivers represent privileged system software with kernel-level access. Verify download sources and check digital signatures. Compromised drivers create severe security vulnerabilities.
No single driver update solution serves all requirements optimally. Technical users benefit from SDI Origin’s transparency and control. Business environments prioritize ITL Driver Updater’s certification focus. Home users find value in Driver Easy’s balance of simplicity and capability.